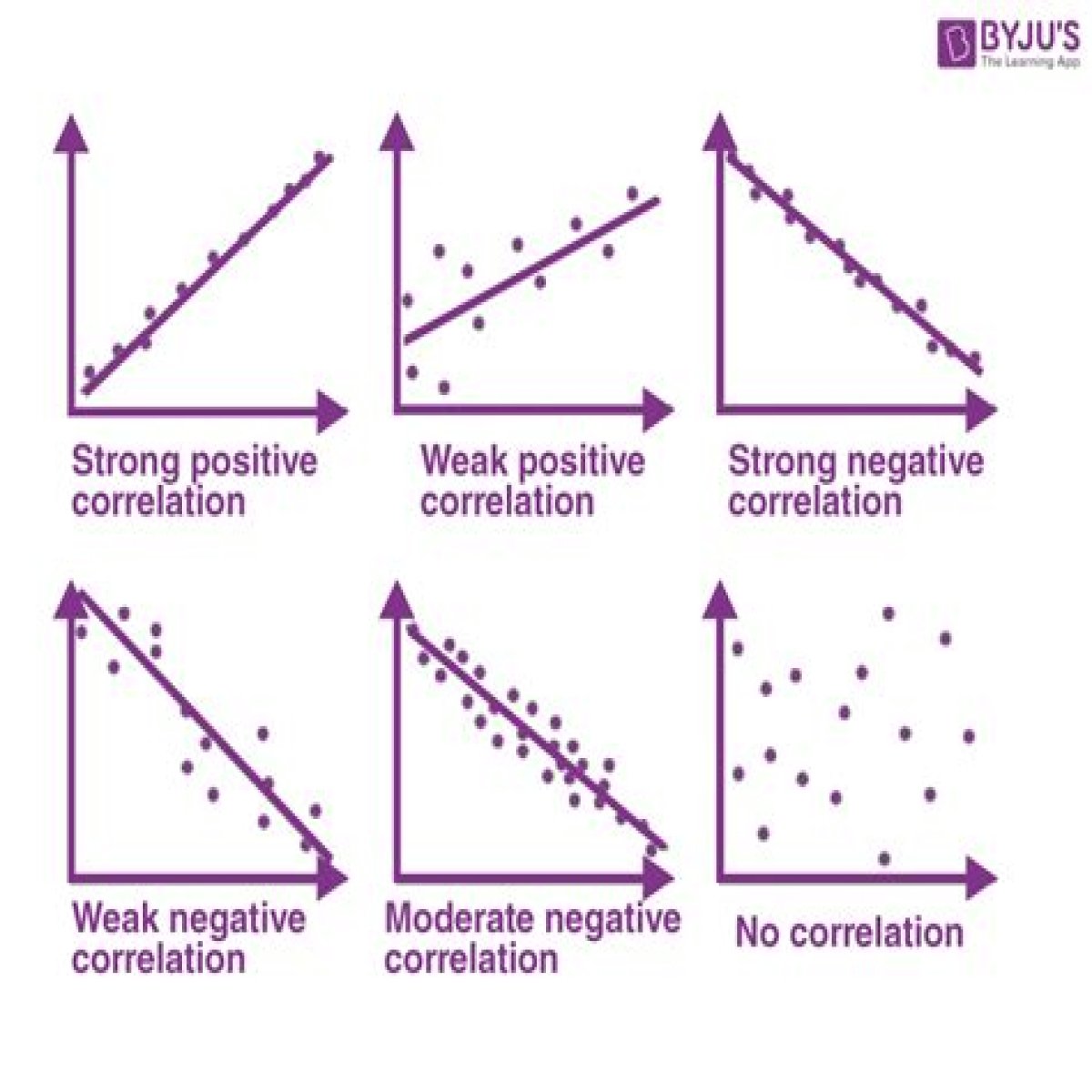
What are the 3 types of correlation in math?
There are three basic types of correlation: positive correlation: the two variables change in the same direction. negative correlation: the two variables change in opposite directions….What are the 3 types of correlation?
- Positive Correlation: r > 0.
- Negative Correlation: r < 0.
- No correlation: r = 0.
What are the 5 types of correlation?
Types of Correlation:
- Positive, Negative or Zero Correlation:
- Linear or Curvilinear Correlation:
- Scatter Diagram Method:
- Pearson’s Product Moment Co-efficient of Correlation:
- Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient:
What are the 4 types of correlation?
Usually, in statistics, we measure four types of correlations: Pearson correlation, Kendall rank correlation, Spearman correlation, and the Point-Biserial correlation.
What are the different correlations in maths?
Correlation in maths Data sets have a positive correlation when they increase together, and a negative correlation when one set increases as the other decreases.
Why are there different types of correlations?
Different kinds of correlations are used in statistics to measure the ways variables relate to one another. The type of correlation performed depends on whether the variables are non-numeric or interval data, such as temperature.
What are the different methods of finding correlation?
Methods of Determining Correlation
- Scatter Diagram Method.
- Karl Pearson’s Coefficient of Correlation.
- Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient; and.
- Methods of Least Squares.
How do you know what type of correlation?
When the y variable tends to increase as the x variable increases, we say there is a positive correlation between the variables. When the y variable tends to decrease as the x variable increases, we say there is a negative correlation between the variables.
What is a correlation coefficient in math?
The correlation coefficient is a statistical measure of the strength of the relationship between the relative movements of two variables. The values range between -1.0 and 1.0.
What is Karl Pearson coefficient of correlation?
Karl Pearson’s coefficient of correlation is defined as a linear correlation coefficient that falls in the value range of -1 to +1. Value of -1 signifies strong negative correlation while +1 indicates strong positive correlation.
What are the assumptions of Pearson’s correlation?
The assumptions are as follows: level of measurement, related pairs, absence of outliers, and linearity. Level of measurement refers to each variable. For a Pearson correlation, each variable should be continuous.
What is Karl Pearson’s coefficient of correlation?
How do you find the correlation coefficient in math?
Here are the steps to take in calculating the correlation coefficient:
- Determine your data sets.
- Calculate the standardized value for your x variables.
- Calculate the standardized value for your y variables.
- Multiply and find the sum.
- Divide the sum and determine the correlation coefficient.